Successful cybercriminals rely on secure, undetectable and resilient infrastructure. Beneath every instance of network compromise, stolen credentials, ransomware, or data theft and sale on illicit forums, is secure infrastructure that enables cybercriminals to operate and remain hidden.
However, for cybercriminals, remaining undetectable and difficult to trace is increasingly a challenge. Global collaboration between governments, law enforcement, and the private sector is making it harder for them to remain anonymous online. Further, very few cybercriminals have the skills and expertise required to manage and maintain secure infrastructure on their own. As such, they seek out illicit infrastructure providers who can deliver this service on their behalf, enabling the cybercriminal to focus on victims and profit.
'Cybercrime-as-a-service' refers to the underground market that has developed to support a range of malicious actors. This underground market comprises of an ever-increasing and evolving range of purchasable tools, services, and information that assists cybercriminals in victimising online targets. Would be cybercriminals can buy access to networks, purchase tools to assist in evading security measures, as well as buy malware to deploy against victims and steal personal information. Bulletproof hosting (BPH) providers are a part of this ecosystem and offer secure infrastructure to cybercriminals. Importantly, one BPH provider can directly enable hundreds of cybercriminals to target victims across the globe.
What is a "Bulletproof" hosting provider?
Simply put, BPH providers lease cybercriminals a virtual and/or physical infrastructure from which to operate. BPH providers are a specific class of internet infrastructure service that enables malicious actors (including cybercriminals) to host illicit content and run operations on the internet.
The term "bulletproof" is pure marketing. In reality, these services are as equally susceptible to disruption as other infrastructure providers. Instead, BPH providers refuse to abide by law enforcement and other content takedown requests and ignore abuse complaints from victims and subscriber request notices. This means cybercriminals can communicate, run illicit forums and websites, deploy malware and phishing campaigns, and launder money without fear that the operator will terminate their lease at law enforcement or other requests.
BPH providers knowingly participate in the cybercrime ecosystem and enable serious financially motivated cybercrime. Major cyber security incidents affecting Australian organisations and their customers have occurred as a result of criminals leveraging BPH providers. Consequences of these incidents have included disruptive ransomware attacks, data extortion and theft of sensitive information.
Representation of a bulletproof hosting provider advertisement in underground forums:

New offer!
Secure & Uncensored Hosting
Looking for BPH service now? We tailor our services for our customers and for reasonable pricing will work with you to get what you need. We will respect your privacy and don't care about your activity!
Standard BPH Service Offerings
- Proxy networks to obfuscate client activity
- Back-end hosting
- Admin/Support
- TLS Certs
- Domain Registration
- Hosting outside of reach from police and government
- C2 infrastructure for malware operations
- Botnet C2 servers
- Cybercrime marketplaces & forums for your business
Host your Dedicated Leak Site here. We won't get taken down!
Payment methods: BITCOIN, TETHER, ETHEREUM, LITECOIN
How do BPH providers work?
The business model differs between BPH providers. The most common method involves leasing IP addresses to cybercriminal customers and using complex network switching methods to help obscure their locations, identities and activities. In many cases, BPH providers resell or lease IP addresses and servers from other legitimate hosting providers, data centres or Internet Service Providers (ISPs). These 'upstream' providers may be unaware they are providing infrastructure to BPH providers who then provide services ‘downstream’ to cybercriminals.
BPH providers configure their networks and system architecture to make it harder to identify their customers. For example, they frequently change the internet facing identifiers associated with the customer’s activity – such as their assigned IP addresses and domain name. Such techniques challenge defenders and investigators by making it harder to link an incident and an IP address being used by an actor or customer at any given time. Additionally, BPH providers often use infrastructure in countries with permissive cyber regimes, where formal measures to investigate and prevent malicious cyber activity are either non-existent or lenient.
How are bulletproof hosting providers different to legitimate infrastructure providers?
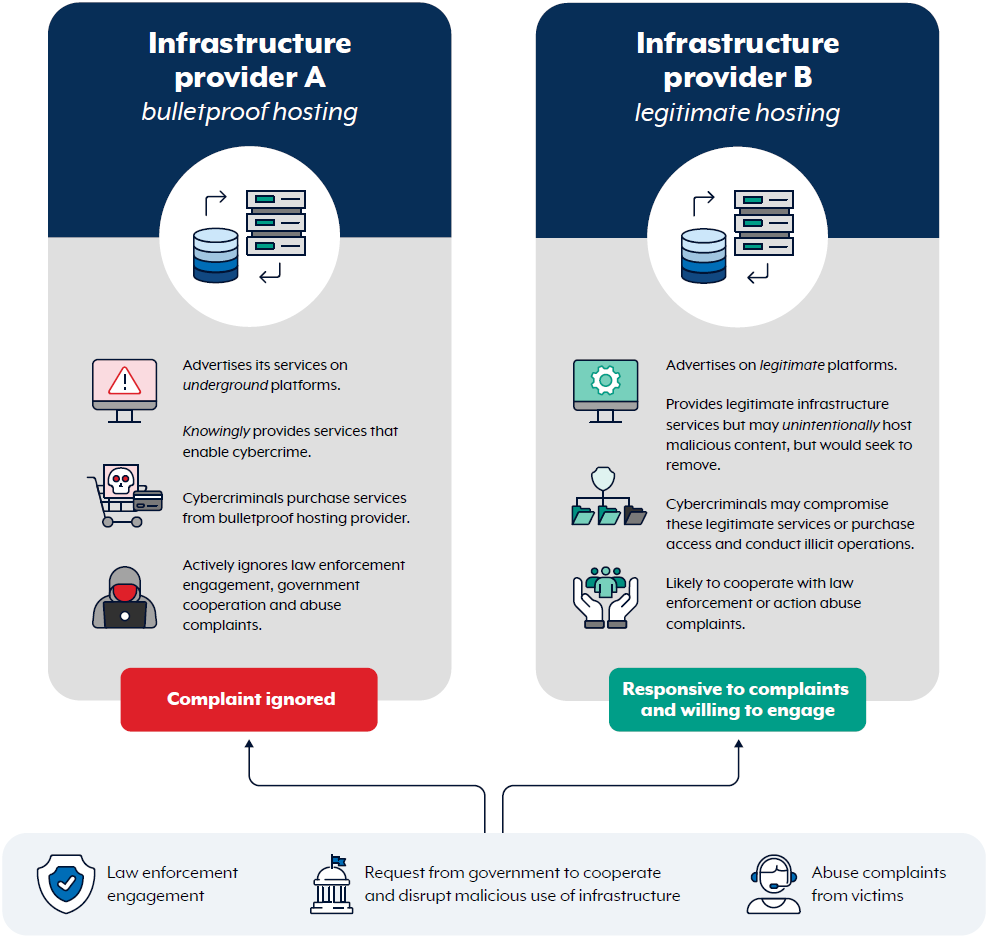
Infrastructure provider A (bulletproof hosting)
- Advertises its services on underground platforms.
- Knowingly provides services that enable cybercrime.
- Cybercriminals purchase services from bulletproof hosting provider.
- Actively ignores law enforcement engagement, government cooperation and abuse complaints.
- Complaints ignored
- Law enforcement engagement
- Request from government to cooperate and disrupt malicious use of infrastructure
- Abuse complaints from victims
Infrastructure provider B (legitimate hosting)
- Advertises on legitimate platforms.
- Provides legitimate infrastructure services but may unintentionally host malicious content, but would seek to remove.
- Cybercriminals may compromise these legitimate services or purchase access and conduct illicit operations.
- Likely to cooperate with law enforcement or action abuse complaints.
- Responsive to complaints and willing to engage
- Law enforcement engagement
- Request from government to cooperate and disrupt malicious use of infrastructure
- Abuse complaints from victims
How targeting BPH providers impacts the cybercrime threat
BPH providers represent a valuable opportunity to disrupt hundreds to thousands of cybercriminals at once. A range of cybercriminals and other malicious actors use these services to make their offending easier – trusting that their activity will remain obfuscated and operational in the face of takedown requests or abuse complaints.
However, law enforcement, Government agencies, and the private sector are collaborating to target and disrupt these illicit infrastructure providers, including through Defensive measures such as proactively blocking internet traffic from known BPH providers. These activities help to reduce the amount of cybercrime interacting with Australian and allied networks, and include legitimate 'upstream' infrastructure providers and ISPs who may be unknowingly enabling BPH providers to access the internet and provide secure infrastructure to cybercriminals.
BPH providers are not the only category of infrastructure provider within the cybercrime-as-a-service ecosystem. These services perpetuate and enable the cybercrime threat to Australia by actively supporting cybercriminal campaigns and deliberately impeding lawful investigation and response. Taking action against BPH providers highlights the vulnerability of these services and the malicious actors who use them.
